| Vienna Wien | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||
| Coordinates: 48°12′32″N 16°22′21″E | |||||
| Country | Austria | ||||
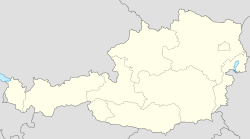
| State | Wien, Capital City | ||||
| Government | |||||
| - Mayor andgovernor | Michael Häupl (SPÖ) | ||||
| Area | |||||
| - City | 414.90 km2 (160.2 sq mi) | ||||
| - Land | 395.51 km2 (152.7 sq mi) | ||||
| - Water | 19.39 km2 (7.5 sq mi) | ||||
| Elevation | 190 m (623 ft) | ||||
| Population (2010) | |||||
| - City | 1,698,822 | ||||
| - Density | 4,094.5/km2 (10,604.8/sq mi) | ||||
| - Urban | 1,996,885 | ||||
| - Metro | 2,268,656 | ||||
| Statistik Austria | |||||
| Time zone | CET (UTC+1) | ||||
| - Summer (DST) | CEST (UTC+2) | ||||
| Website | www.wien.at | ||||
.
Vienna lies in the east of Austria and is close to the borders of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, and Hungary. These regions work together in a European Centrope border region. Along with nearby Bratislava, Vienna forms a metropolitan region of 3 million inhabitants, referred to as Twin City. In 2001, the city centre was designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
In a 2005 study of 127 world cities, the Economist Intelligence Unit ranked the city first (in a tie with Vancouver) for quality of life. This assessment was mirrored by the Mercer Survey in 2009 and 2010. Analytically, the city was ranked 1st globally for a culture of innovation in 2007 and 2008, and 2nd globally after Boston in 2009 from 256 cities on an analysis of 162 indicators in the Innovation Cities Index on a 3 factor score covering culture, infrastructure and markets. As a city, Vienna regularly hosts urban planning conferences and is often used as a case study by urban planners.
The city rates highly in popular opinion-based journalistic rankings from magazines such as Monocle, where it's rated 5th in 2010.
Name
The English name of Vienna, the official German name Wien, and the names of the city in most languages, are thought to be derived from the Celtic name of a settlement, but opinions vary on the precise origin. Some claim that the name comes from Vedunia, meaning "forest stream," which subsequently became Venia, Wienne and Wien. Others claim that the name comes from the name of the Roman settlement Vindobona, probably meaning "white base/bottom," which became Vindovina, Vídeň (Czech) and Wien.
The name of the city in Hungarian (Bécs), Bosnian, Croatian and Serbian (Beč) and Ottoman Turkish (Beç) appears to have a different, Slavonic, origin. In Slovene, the city is called Dunaj which in other Slavic languages means the Danube river.
History
History of Vienna
Roman ruins at Michaelerplatz
Vienna in 1493 (from the Nuremberg Chronicle).
Early history
Founded around 500 BC, Vienna was originally a Celtic settlement. In 15 BC, Vienna became a Roman frontier city (Vindobona) guarding the Roman Empire against Germanic tribes to the north.
The Mongols at the Gates of Vienna
In the 13th century, Vienna came under threat from the Mongolian Empire, which stretched over much of present-day Russia and China. However, due to the death of its leader, Ogedei Khan, the Mongolian armies receded from the European frontier and did not return.
The Habsburgs and the Holy Roman Empire
During the Middle Ages, Vienna was home to the Babenberg Dynasty, and in 1440, it became the resident city of the Habsburg Dynasties. It eventually grew to become the capital of the Holy Roman Empire and a cultural centre for arts and science, music and fine cuisine. It was occupied by Hungary between 1485-1490. In the 16th and 17th centuries, the Ottoman armies were stopped twice outside Vienna (see Siege of Vienna, 1529 and Battle of Vienna, 1683). In 1679 the bubonic plague struck the city, killing nearly a third of its population.
Vienna map, 1773-81
View of Vienna in 1758, by Bernardo Bellotto
Collapse of the Holy Roman Empire
In 1804, during the Napoleonic wars, Vienna became the capital of the Austrian Empire and continued to play a major role in European and world politics, including hosting the 1814 Congress of Vienna. After the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of 1867, Vienna remained the capital of what was then the Austro-Hungarian Empire. The city was a centre of classical music, for which the title of the First Viennese School is sometimes applied. During the latter half of the 19th century, the city developed what had previously been the bastions and glacis into the Ringstraße, a new boulevard surrounding the historical town and a major prestige project. Former suburbs were incorporated, and the city of Vienna grew dramatically. In 1918, after World War I, Vienna became capital of the First Austrian Republic.
From the late 19th century to 1938, the city remained a centre of high culture and later modernism. A world capital of music, the city played host to composers such as Brahms, Bruckner, Mahler and Richard Strauss. The city's cultural contributions in the first half of the 20th century included, amongst many, the Vienna Secession movement, psychoanalysis, the Second Viennese School, the architecture of Adolf Loos and the philosophy of Ludwig Wittgenstein. Within Austria, it was seen as a centre of socialist politics, for which it was sometimes referred to as "Red Vienna". The city was a stage to the Austrian Civil War of 1934, when Chancellor Engelbert Dollfuss sent the Austrian Army to shell civilian housing occupied by the socialist militia.
Vienna in 1900
The Anschluss and World War II
In 1938, after a triumphant entry into Austria, Adolf Hitler famously spoke to the Austrian people from the balcony of the Neue Burg, a part of the Hofburg at the Heldenplatz. Between 1938 (see Anschluss) and the end of the Second World War, Vienna lost its status as a capital to Berlin. On 2 April 1945, the Soviets launched the Vienna Offensive against the Germans holding the city and besieging it. British and American air raids, and artillery duels between the Wehrmacht and the Red Army, crippled infrastructure such as tram services and water and power distribution, and destroyed or damaged thousands of public and private buildings. Vienna fell two weeks later. Austria was then separated from Germany, and Vienna was restored as the republic's capital city.
Four Power Vienna
After the war, Vienna lay deep inside the Soviet occupied zone of Austria, and just like in the case of Berlin, Vienna itself was divided into sectors by the four prevailing nations and supervised by an Allied Commission.
Occupation zones in Vienna, 1945-1955
The four power occupation of Vienna differed in one key respect from that of Berlin in that the central area of the city, known as the first district, constituted an international zone in which the four powers alternated control on a monthly basis. The Berlin Blockade of 1948 raised concerns that the Russians might repeat the blockade in Vienna. The matter was raised in the House of Commons of the United Kingdom,
"What plans have the Government for dealing with a similar situation in Vienna? Vienna is in exactly a similar position to Berlin. It is surrounded by a Soviet Zone of occupation and we have our sector of responsibility in Vienna the same as the Americans and the French. What plans have the Government to deal with a similar situation arising in Vienna in the near future? I hope we shall have an answer, because this is of vital importance." Sir Anthony Nutting, Honourable Member for Melton, 30 June 1948, House of Commons, London.
The situation in Vienna would have been even more precarious than in Berlin due to a lack of airfields in the Western sectors, and as such, contingency plans were drafted by the authorities. These contingency plans included the laying down of metal landing mats at Schönbrunn. However, despite fears and some disruptions, the Soviets did not embark on a wholesale blockade of the city as they did with Berlin. Some have argued that this was because the Potsdam Agreement gave written rights of land access to the western sectors, whereas no such written guarantees had been given regarding the western sectors of Berlin. During the 10 years of the four power occupation, Vienna became a hot-bed for international espionage between the Western and Eastern blocs. However, unlike in the case of four power Berlin, the cold war in Vienna took on a different dynamic in the wake of the Berlin Blockade. The Russians, while accepting that Germany and Berlin would be divided, had decided that it was not in their interests that the same state of affairs should arise in Austria and Vienna. When the first barbed wire fences went up around the perimeter of West Berlin in 1953, no such actions were reciprocated in Vienna, and by 1955, the Russians had agreed to relinquish their occupation zones in Eastern Austria, and East Vienna, as well as their sector in the fourth and tenth districts in South Vienna, in exchange for a permanent neutrality clause to be enshrined into the new Austrian State Treaty. Hence in 1955, the Russians pulled out of Austria, and Vienna was spared the drama of the wall which would beset Berlin six years later. The atmosphere of four power Vienna is captured in the Graham Greene novel The Third Man, and by the movie which followed in 1949.
The State Treaty
The four power control of Vienna lasted until the Austrian State Treaty was signed in 1955, and it was not until then, following years of reconstruction and restoration, that the State Opera and the Burgtheater, both on the Ringstraße, reopened to the public. The State Treaty ensured that modern Austria would align with neither NATO nor the Soviet block, and it is seen as one of the reasons for Austria's late entry into the European Union. In the 1970s, Austrian Chancellor Bruno Kreisky inaugurated the Vienna International Centre, a new area of the city created to host international institutions. Vienna has regained a part of its former international relevance by hosting international organizations, such as the United Nations (United Nations Industrial Development Organization, United Nations Office at Vienna, Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization and United Nations Office on Drugs and Crime), the International Atomic Energy Agency, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries, and the Organization for Security and Cooperation in Europe.
Historical population
Inhabitants according to official census figures: 1800 to 2005
Due to the industrialization and immigration from other parts of the Empire, the population of Vienna increased sharply during its time as the capital of Austria-Hungary (1867–1918). In 1910, Vienna had more than two million inhabitants, and was one of the six largest cities in the world.[citation needed] At the turn of the century, Vienna (Czech Vídeň, Hungarian Bécs) was the city with the second largest Czech population in the world (after Prague). At the height of the migration, about one-third of the Viennese population was of Slavic or Hungarian origin. However, after World War I, many Czechs and Hungarians returned to their ancestral countries, resulting in a decline in the Viennese population. In 1923 there were 201,513 Jews living in Vienna, which had become the third largest Jewish community in Europe.
By 2001, 16% of people under the census living in Austria had nationalities other than Austrian, nearly half of whom were from former Yugoslavia, primarily Serbs; the next most numerous nationalities in Vienna were Turkish (39,000 or 2.5%), Polish (13,600 or 0.9%) and German (12,700 or 0.8%).
| Year | 1754 | 1800 | 1850 | 1900 | 1910 | 1923 | 1939 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total population | 175,460 | 271,800 | 551,300 | 1,769,137 | 2,083,630 | 1,918,720 | 1,770,938 |
| Year | 1951 | 1961 | 1971 | 1981 | 1991 | 2001 | 2008 |
| Total population | 1,616,125 | 1,627,566 | 1,619,885 | 1,531,346 | 1,539,848 | 1,550,123 | 1,678,435 |
Geography and climate
Vienna is located in northeastern Austria, at the easternmost extension of the Alps in the Vienna Basin. The earliest settlement, at the location of today's inner city, was south of the meandering Danube while the city now spans both sides of the river. Elevation ranges from 151 to 524 m (495 to 1,719 ft).
Vienna has an oceanic climate according to the Köppen classification. The city has warm summers with average high temperatures of 22 to 26 °C (72 to 79 °F), with maxima exceeding 30 °C (86 °F) and lows of around 15 °C (59 °F). Winters are relatively cold with average temperatures at about freezing point, and snowfall occurring mainly from December through March. Spring and autumn are cool to mild. Precipitation is generally moderate throughout the year, averaging 620 mm (24.4 inches) annually.
| Climate data for Vienna, Austria (1971-2000) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Average high °C (°F) | 2.9 (37.2) | 5.1 (41.2) | 10.3 (50.5) | 15.2 (59.4) | 20.5 (68.9) | 23.4 (74.1) | 25.6 (78.1) | 25.4 (77.7) | 20.3 (68.5) | 14.2 (57.6) | 7.5 (45.5) | 4.0 (39.2) | 14.53 (58.16) |
| Average low °C (°F) | -2.0 (28.4) | -0.9 (30.4) | 2.4 (36.3) | 5.8 (42.4) | 10.5 (50.9) | 13.5 (56.3) | 15.4 (59.7) | 15.3 (59.5) | 11.7 (53.1) | 7.0 (44.6) | 2.4 (36.3) | -0.5 (31.1) | 6.72 (44.09) |
| Precipitation mm (inches) | 37.2 (1.465) | 39.4 (1.551) | 46.1 (1.815) | 51.7 (2.035) | 61.8 (2.433) | 70.2 (2.764) | 68.2 (2.685) | 57.8 (2.276) | 53.5 (2.106) | 40.0 (1.575) | 50.0 (1.969) | 44.4 (1.748) | 620.3 (24.421) |
| Source: World Weather Information Service | |||||||||||||
Districts and enlargement
Districts of Vienna
Map of the districts of Vienna with numbers
Satellite view of Vienna
Vienna is composed of 23 districts (Bezirke). Administrative district offices in Vienna (called Magistratisches Bezirksamt) serve similar to those in the other states (called Bezirkshauptmannschaft), the officers being subject to the Landeshauptmann (which in Vienna is the mayor); with the exception of the police, which in Vienna is governed by the President of the Police (at the same time one of the nine Directors of Security of Austria), a federal office, directly responsible to the Minister of the Interior.
As had been planned in 1919 for all of Austria but not introduced, the district residents in Vienna (Austrians as well as EU citizens with permanent residence here) are electing a District Assembly (Bezirksvertretung) which chooses the District Head (Bezirksvorsteher) as political representative of the district on city level. The district assemblies have been given some political power by city hall in fields such as planning, building and traffic. City hall has delegated maintenance budgets, e.g., for schools, parks and secondary streets, to the district assemblies, so that they are able to set priorities autonomously. Any decision of a district can be overridden by the city assembly (Gemeinderat) or the responsible city councillor (amtsführender Stadrat).
The heart and historical city of Vienna, a large part of today's Innere Stadt, was once surrounded by walls and open fields in order to defend itself from potential attackers. In 1850, Vienna with the consent of the emperor included 34 surrounding villages, called Vorstädte, into the city limits (districts no. 2 to 8, since 1861 with the separation of Margareten from Wieden no. 2 to 9). Consequently the walls were razed after 1857, making it possible for the city centre to expand.
In their place, a broad boulevard called the Ringstraße was built, along which imposing public and private buildings, monuments, and parks were created until the turn of the century. These buildings include the Rathaus (town hall), the Burgtheater, the University, the Parliament, the twin museums of natural history and fine art, and the Staatsoper. It is also the location of New Wing of the Hofburg, the former imperial palace, and the Imperial and Royal War Ministry finished in 1913. The mainly Gothic Stephansdom is located at the centre of the city, on Stephansplatz. The Imperial-Royal Government set up the Vienna City Renovation Fund (Wiener Stadterneuerungsfonds) and sold many building lots to private investors, thereby partly financing public construction works.
From 1850 to 1890, city limits in the West and the South have mainly followed another wall called Linienwall. Outside this wall from 1873 onwards a ring road called Gürtel was built. In 1890 it was decided to integrate 33 suburbs (called Vororte) beyond that wall into Vienna by 1 January 1892 and transform them into districts no. 11 to 19 (district no. 10 had been constituted in 1874); hence the Linienwall was torn down from 1894 onwards. In 1900, district no. 20, Brigittenau, was created by separating the area from the 2nd district.
From 1850 to 1904, Vienna had expanded only on the right bank of the Danube, following the main branch before the regulation of 1868−1875, i.e., the Old Danube of today. In 1904, the 21st district was created by integrating Floridsdorf, Kagran, Stadlau, Hirschstetten, Aspern and other villages on the left bank of the Danube into Vienna, in 1910 Strebersdorf followed. On 15 October 1938 the Nazis created Great Vienna with 26 districts by merging 97 cities and villages into Vienna, 80 of which have returned to surrounding Lower Austria in 1954. Since then Vienna has 23 districts.
Industries are located mostly in the southern and eastern districts. The Innere Stadt is situated away from the main flow of the Danube, but is bounded by the Donaukanal ("Danube canal"). Vienna's second and twentieth districts are located between the Donaukanal and the Danube River. Across the Danube, where the Vienna International Centre is located, and in the southernmost area are the newest parts of the city (districts 21−23).
Politics
The Rathaus serves as the seat of the mayor and city council of the city of Vienna. In the picture Rathaus square in Christmas period
Until 1918, Viennese politics were shaped by the Christian Social Party, in particular long-term mayor Karl Lueger. Vienna is today considered the centre of the Social Democratic Party of Austria. During the period of the First Republic (1918–1934), the Vienna Social Democrats undertook many overdue social reforms. At that time, Vienna's municipal policy was admired by Socialists throughout Europe, who therefore referred to the city as "Red Vienna" (Rotes Wien). In February 1934 troops of the Conservative Austrian federal government and paramilitary socialist organisations were engaged in the Austrian civil war, which led to the ban of the Social Democrat party.
For most of the time since the First World War, the city has been governed by the Social Democratic Party (SPÖ) with absolute majorities in the city parliament. Only between 1934 and 1945, when the Social Democratic Party was illegal, mayors were appointed by the austro-fascist and later by the Nazi authorities. The current mayor of Vienna is Michael Häupl. The Social Democrats currently hold 55% of the seats with a 49% share of the vote. Many Austrian political experts[who?] believe that if not for the Social Democrats' nearly unbreakable hold on Vienna, the rival Austrian People's Party (ÖVP) would dominate Austrian politics.
An example of the city’s many social democratic policies is its low-cost residential estates called Gemeindebauten.
Ever since Vienna obtained federal state (Bundesland) status of its own in 1921, the mayor has also had the role of the state governor (Landeshauptmann). The Rathaus accommodates the offices of the mayor and the state government (Landesregierung). The city is administered by a multitude of departments (Magistratsabteilungen).
In the 1996 City Council election, the SPÖ lost its overall majority in the 100-seat chamber, winning 43 seats and 39.15% of the vote. In 1996 the Freedom Party of Austria (FPÖ), which won 29 seats (up from 21 in 1991), beat the ÖVP into third place for the second time running. From 1996-2001, the SPÖ governed Vienna in a coalition with the ÖVP. In 2001 the SPÖ regained the overall majority with 52 seats and 46.91% of the vote; in October 2005 this majority was increased further to 55 seats (49.09%). In course of the 2010 city council elections the SPÖ lost their overall majority again and consequently forged a coalition with the Green Party - the first SPÖ/Green coalition in Austria.
Religions
St. Stephen's Cathedral (Stephansdom) in 1895
Vienna is the seat of the Viennese Roman Catholic archdiocese, and its current Archbishop is Cardinal Christoph Schönborn. The religions of the Viennese resident population is divided according to the 2001 census as follows :
Roman Catholic 49.2%
No religion 25.7%
Muslim 7.8%
Orthodox 6.0%
Protestant (mostly Lutheran) 4.7%
Jewish 0.5%
Other or none indicated 6.3%
Many Roman Catholic churches in central Vienna also feature performances of religious or other music, including masses sung with classical music and organ. Some of Vienna's most significant historical buildings are Roman Catholic churches, including the Stephansdom (St. Stephen's Cathedral), the Karlskirche (St. Charles' Church) and the Votivkirche.
Culture
Music, theatre and opera
Music of Austria and Vienna State Opera Ballet
State Opera (Staatsoper)
Hofburg Palace
Kunsthistorisches Museum at Maria-Theresa-Square
Austrian Museum of Applied Arts
Art and culture have a longtradition in Vienna, including theater, opera, classical music and fine arts. The Burgtheater is considered one of the best theaters in the German-speaking world alongside its branch, the Akademietheater. The Volkstheater Wien and the Theater in der Josefstadt also enjoy good reputations. There is also a multitude of smaller theaters, in many cases devoted to less mainstream forms of performing arts, such as modern, experimental plays or cabaret.
Vienna is also home to a number of opera houses, including the Theater an der Wien, the Staatsoper and the Volksoper, the latter being devoted to the typical Viennese operetta. Classical concerts are performed at well known venues such as the Wiener Musikverein, home of the Vienna Philharmonic Orchestra, and the Wiener Konzerthaus. Many concert venues offer concerts aimed at tourists, featuring popular highlights of Viennese music (particularly the works of Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart and Johann Strauss).
In recent years, the Theater an der Wien has become widely known for hosting premieres of musicals, although it has recently devoted itself to the opera again. The most successful musical by far was "Elisabeth", which was later translated into several other languages and performed all over the world. The Haus der Musik ("house of music") opened in 2000.
Museums
The Hofburg is the location of the Schatzkammer (treasury), holding the imperial jewels of the Habsburg dynasty. The Sisi Museum (a museum devoted to Empress Elisabeth Amalie Eugenie of Austria) allows visitors to view the imperial apartments as well as the silver cabinet. Directly opposite the Hofburg are the Kunsthistorisches Museum, which houses many paintings by old masters, ancient and classical artifacts, and the Naturhistorisches Museum.
A number of museums are located in the Museumsquartier (museum quarter), the former Imperial Stalls which were converted into a museum complex in the 1990s. It houses the Museum of Modern Art, commonly known as the MUMOK (Ludwig Foundation), the Leopold Museum (featuring the largest collection of paintings in the world by Egon Schiele, as well as works by the Vienna Secession, Viennese Modernism and Austrian Expressionism), the AzW (museum of architecture), additional halls with feature exhibitions, and the Tanzquartier. The Liechtenstein Palace contains one of the world's largest private art collections of the baroque. Castle Belvedere, built under Prinz Eugen, has a gallery containing paintings by Gustav Klimt (The Kiss), Egon Schiele, and other painters of the early 20th century, also sculptures by Franz Xaver Messerschmidt, and changing exhibitions too.
There are a multitude of other museums in Vienna, including the Albertina, the Military History Museum, the Technical Museum, the Vienna Clock Museum, the Burial Museum, the Museum of Art Fakes, the KunstHausWien, the Sigmund Freud Museum, and the Mozarthaus Vienna. The museums dedicated to Vienna's districts provide a retrospective of the respective districts.
Architecture
Category:Buildings and structures in Austria
Center of Vienna architecture
A variety of architectural styles can be found in Vienna, such as the Romanesque Ruprechtskirche and the Baroque Karlskirche. Styles range from classicist buildings to modern architecture. Art Nouveau left many architectural traces in Vienna. The Secession, Karlsplatz Stadtbahn Station, and the Kirche am Steinhof by Otto Wagner rank among the best known examples of Art Nouveau in the world.
Palais Ferstl
The Hundertwasserhaus by Friedensreich Hundertwasser, designed to counter the clinical look of modern architecture, is one of Vienna's most popular tourist attractions. Another example of unique architecture is the Wotrubakirche by sculptor Fritz Wotruba. In the 1990s, a number of quarters were adapted and extensive building projects were implemented in the areas around Donaustadt (north of the Danube) and Wienerberg (in southern Vienna). The 202 m-high Millennium Tower located at Handelskai is the highest building in Vienna. In recent years, Vienna has seen numerous architecture projects completed which combine modern architectural elements with old buildings, such as the remodelling and revitalisation of the old Gasometer in 2001. Most buildings in Vienna are relatively low; in early 2006 there were around 100 buildings higher than 40 m. The number of high-rise buildings is kept low by building legislation aimed at preserving green areas and districts designated as world cultural heritage. Strong rules apply to the planning, authorisation and construction of high-rise buildings. Consequently, much of the inner city is a high-rise free zone.
Vienna balls
Vienna is the last great capital of the nineteenth century ball. There are over 200 significant balls per year, some featuring as many as nine live orchestras. Balls are held in the many beautiful palaces in Vienna, with the principal venue being the Hofburg Palace at Heldenplatz. While the Opera Ball is the best known internationally of all the Austrian balls, other balls such as the Kaffeesiederball (Cafe Owners Ball), the Jägerball (Hunter's Ball) and the Rudolfina Redoute are almost as well known within Austria and even better appreciated for their cordial atmosphere. Viennese of at least middle class may visit a number of balls in their lifetime. For many, the ball season lasts three months and can include up to ten or fifteen separate appearances.
Dancers and opera singers from the Vienna Staatsoper often perform at the openings of the larger balls.
A Vienna ball is an all-night cultural attraction. Major Viennese balls generally begin at 9pm and last until 5am, although many guests carry on the celebrations into the next day.
Education
Vienna is also Austria's main centre of education and home to many universities, professional colleges and gymnasiums.
Vienna University of Technology
Academy of Fine Arts
Universities
Academy of Fine Arts Vienna
Diplomatic Academy of Vienna
Medical University of Vienna
PEF Private University of Management Vienna
University of Applied Arts Vienna
University of Music and Performing Arts, Vienna
University of Veterinary Medicine Vienna
University of Vienna
Vienna University of Economics and Business
University of Natural Resources and Applied Life Sciences, Vienna
Vienna University of Technology
Webster University Vienna
International schools
American International School Vienna
Danube International School
International University Vienna
Lycée Français de Vienne
Vienna Christian School
Vienna International School
Transportation
Stephansplatz (Vienna U-Bahn) metro station
Vienna has an extensive transportation network. Public transport is provided by buses, trams, and 5 subway lines (U-Bahn). Trains are operated by the ÖBB. Vienna has multiple road connections, including motorways.
Vienna is served by Vienna International Airport, located 18 km (11.18 mi) southeast of the city centre next to the town of Schwechat.
Leisure activities
Viennese parks and gardens
Vienna city park
Vienna possesses many park facilities, including the Stadtpark, the Burggarten, the Volksgarten (part of the Hofburg), the Schloßpark at Schloss Belvedere (home to the Vienna Botanic Gardens), the Donaupark, the Schönbrunner Schlosspark, the Prater, the Augarten, the Rathauspark, the Lainzer Tiergarten, the Dehnepark, the Resselpark, the Votivpark, the Kurpark Oberlaa, the Auer-Welsbach-Park and the Türkenschanzpark. Green areas include Laaer-Berg (including the Bohemian Prater) and the foothills of the Wienerwald, which reaches into the outer areas of the city. Small parks, known by the Viennese as Beserlparks, are everywhere in the inner city areas. Many of Vienna's famous parks include monuments, such as the Stadtpark with its statue of Johann Strauss II, and the gardens of the baroque palace, where the State Treaty was signed. Vienna's principal park is the Prater which is home to the Riesenrad, a Ferris wheel. The imperial Schönbrunn's grounds contain an 18th century park which includes the world's oldest zoo, founded in 1752. The Donauinsel, part of Vienna's flood defences, is a 21.1 km long artificial island between the Danube and Neue Donau dedicated to leisure activities.
Sport
Ernst-Happel-Stadion in the Prater
Vienna hosts many different sporting events including the Vienna City Marathon, which attracts more than 10,000 participants every year and normally takes place in May. In 2005 the Ice Hockey World Championships took place in Austria and the final was played in Vienna. Vienna's Ernst Happel Stadium was the venue of four Champions League and European Champion Clubs' Cup finals (1964, 1987, 1990 and 1995) and on June 29 it hosted the final of Euro 2008 which saw a Spanish 1-0 victory over Germany.
Austria's capital is home to numerous teams. The best known are the local football clubs SK Rapid Wien (32 Austrian Bundesliga titles), FK Austria Wien (23 Austrian Bundesliga titles and 26-time cup winners) and the oldest team, First Vienna FC. Other important sport clubs include the Raiffeisen Vikings Vienna (American Football), who won the Eurobowl title between 2004 and 2007 4 times in a row, the Aon hotVolleys Vienna, one of Europe's premier Volleyball organisations, the Superfund Wanderers (baseball) who won the 2009 Championship of the Austrian Baseball League, and the Vienna Capitals (Ice Hockey). Vienna was also where the European Handball Federation (EHF) was founded.
Culinary specialities
Food
Austrian food
Wiener Schnitzel
Vienna is well known for Wiener Schnitzel, a cutlet of veal that is pounded flat, coated in flour, egg and breadcrumbs, and fried in clarified butter. It is available in almost every restaurant that serves Viennese cuisine. Other examples of Viennese cuisine include Tafelspitz (very lean boiled beef), which is traditionally served with Geröstete Erdäpfel (boiled potatoes mashed with a fork and subsequently fried) and horseradish sauce, Apfelkren (a mixture of horseradish, cream and apple) and Schnittlauchsauce (a chives sauce made with mayonnaise and old bread).
Sachertorte
Vienna has a long tradition of producing the finest cakes and desserts. These include Apfelstrudel (hot apple strudel), Palatschinken (sweet pancakes), and Knödel (dumplings) often filled with fruit such as apricots (Marillenknödel). Sachertorte, a dry chocolate cake with apricot jam created by the Sacher Hotel, is world famous.
In winter, small street stands sell traditional Maroni (hot chestnuts) and potato fritters.
Sausages are popular and available from street vendors (Würstelstand) throughout the day and into the night. The sausage known as Wiener (German for Viennese) in the USA and Germany is, however, called Frankfurter. Other popular sausages are Burenwurst (a coarse beef and pork sausage, generally boiled), Käsekrainer (spicy pork with small chunks of cheese), and Bratwurst (a white pork sausage). Most can be ordered "mit Brot" (with bread) or as a "hot dog" (stuffed inside a long roll). Mustard is the traditional condiment and usually offered in two varieties: "süß" (sweet) or "scharf" (spicy).
Kebab and pizza are, increasingly, the snack food most widely available from small stands.
The Naschmarkt is a permanent market for fruit, vegetables, spices, fish, meat, etc. from around the world. The city centre has many delicatessen stores, such as the Julius Meinl am Graben.
Drink
Vienna, along with Paris, Prague, Bratislava, Warsaw, Barcelona and London is one of the few remaining world capital cities with its own vineyards. The wine is served in small Viennese pubs known as Heuriger, which are especially numerous in the wine growing areas of Döbling (Grinzing, Neustift am Walde, Nußdorf, Salmannsdorf, Sievering), Floridsdorf (Stammersdorf, Strebersdorf) and Liesing (Mauer, Oberlaa). The wine is often drunk as a Spritzer ("G'spritzter") with sparkling water. The Grüner Veltliner, a dry white wine, is the most widely cultivated wine in Austria.
Beer is next in importance to wine. Vienna has a single large brewery, Ottakringer, and more than ten microbreweries. A "Beisl" is a typical small Austrian pub, of which Vienna has many.
Viennese cafés
Demel Café
Viennese cafés have an extremely long and distinguished history that dates back centuries, and the caffeine addictions of some famous historical patrons of the oldest are something of a local legend. Traditionally, the coffee comes with a glass of water. Viennese cafés claim to have invented the process of filtering coffee from bounty captured after the second Turkish siege in 1683. Viennese cafés claim that when the invading Turks left Vienna, they abandoned hundreds of sacks of coffee beans. The Emperor gave Franz George Kolschitzky (Polish - Franciszek Jerzy Kulczycki) some of this coffee as a reward for providing information that allowed the Austrians to defeat the Turks. Kolschitzky then opened Vienna's first coffee shop. Julius Meinl set up a modern roasting plant in the same premises where the coffee sacks were found, in 1891.
Tourist attractions
Tourist attractions in Vienna
Major tourist attractions include the imperial palaces of the Hofburg and Schönbrunn (also home to the world's oldest zoo, Tiergarten Schönbrunn) and the Riesenrad in the Prater. Cultural highlights include the Burgtheater, the Wiener Staatsoper, the Lipizzaner horses at the spanische Hofreitschule and the Vienna Boys' Choir, as well as excursions to Vienna's Heurigen district Döbling.
Panoramic view of world famous Schönbrunn Palace.
There are also more than 100 art museums, which together attract over eight million visitors per year. The most popular ones are Albertina, Belvedere, Leopold Museum in the Museumsquartier, KunstHausWien, BA-CA Kunstforum, the twin Kunsthistorisches Museum and Naturhistorisches Museum, and the Technisches Museum Wien, each of which receives over a quarter of a million visitors per year.
There are many popular sites associated with composers who lived in Vienna including Beethoven's various residences and grave at Zentralfriedhof (Central Cemetery) which is the largest cemetery in Vienna and the burial site of many famous people. Mozart has a memorial grave at the Habsburg gardens and at St. Marx cemetery (where his grave was lost). Vienna's many churches also draw large crowds, the most famous of which are St. Stephen's Cathedral, the Deutschordenskirche, the Jesuitenkirche, the Karlskirche, the Peterskirche, Maria am Gestade, the Minoritenkirche, the Ruprechtskirche, the Schottenkirche and the Votivkirche.
Modern attractions include the Hundertwasserhaus, the United Nations headquarters and the view from the Donauturm.
Schönbrunn Palace
Belvedere Palace
Albertina
Stephansplatz, Vienna
The statue of Athena in front of the Austrian Parliament
The Secession building
The Riesenrad in the Wiener Prater
Modern Vienna
International organizations in Vienna
UN complex in Vienna, with the Austria Center Vienna in front, taken from the Danube Tower in the nearby Donaupark before the extensive building work
Many international organisations and offices are located in Donaustadt
Vienna is the seat of a number of United Nations offices and various international institutions and companies, including the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA), the United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries (OPEC), the Preparatory Commission for the Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organization (CTBTO), the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) and the United Nations Office for Outer Space Affairs (UNOOSA). Currently Vienna is the world's 4th "UN city" (after New York, Geneva and The Hague). Additionally, Vienna is the seat of the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law's secretariat (UNCITRAL). In conjunction, the University of Vienna annually hosts the prestigious Willem C. Vis Moot, an international commercial arbitration competition for students of law from around the world.
Various special diplomatic meetings have been held in Vienna in the latter half of the 20th century, resulting in various documents bearing the name Vienna Convention or Vienna Document. Among the more important documents negotiated in Vienna are the 1969 Vienna Convention on the Law of Treaties, as well as the 1990 Treaty on Conventional Armed Forces in Europe (CFE).
See also: Vienna Convention (disambiguation)
Charitable organizations in Vienna
Alongside the international and intergovernmental organisations, there are dozens of charitable organisations based in Vienna; these organisations provide relief goods and assistance to tens of thousands of disadvantaged children and needy people in developing countries.
One such organisation is the network of SOS Children's Villages, founded by Hermann Gmeiner in 1949. Today, SOS Children's Villages are active in 132 countries and territories worldwide. Others include HASCO and the Childrens Bridge of Hope.
International relations
The Hermesvilla in Hietzing
Twin towns - Sister cities
Vienna is twinned with the following cities:
Belgrade in Serbia
Bratislava in Slovakia
Brno in Czech Republic
Budapest in Hungary
Istanbul in Turkey (since 2007)
Kiev in Ukraine
Ljubljana in Slovenia
Moscow in Russia
Tabriz in Iran (since 2009)
Tel Aviv in Israel
Tunis in Tunisia
Warsaw in Poland (since 2001)
Zagreb in Croatia (since 1994)
Other forms of cooperation and city friendship similar to the twin city programmes:
Niš in Serbia
In addition, individual Viennese districts are twinned with Japanese cities/districts:
Alsergrund with Takarazuka, Hyōgo. (since 1994)
Döbling with Setagaya, Tokyo. (since 1985)
Donaustadt with Arakawa, Tokyo. (since 1996)
Floridsdorf with Katsushika, Tokyo. (since 1987)
Hernals with Fuchu, Tokyo. (since 1992)
Hietzing with Habikino, Osaka. (since 1995)
Innere Stadt with Taito, Tokyo. (since 1989)
Meidling with Gifu, Gifu. (since 1992)
(source:wikipedia)
































No comments:
Post a Comment